Breaking News: Marsquake Unveils Mars’ Thick and Mysterious Crust, Hinting at Volcanic Surprises!
Martian Crust Reveals its Secrets: Uncovering Mars’ Mysteries
In a groundbreaking revelation, planetary scientists have gained unprecedented insights into the enigmatic Martian crust, thanks to the discovery of the most powerful Marsquake ever recorded. Researchers have now confirmed that the average thickness of Mars‘ crust ranges between 42 and 56 kilometers, significantly surpassing the average thickness of Earth’s continental crust by approximately 70 percent. These remarkable findings have been published in an upcoming paper for Geophysical Research Letters.
The pivotal measurements were made possible by NASA‘s InSight lander, a stationary seismometer that diligently recorded seismic waves reverberating through Mars‘ interior for an impressive duration of four Earth years. However, it was last May’s monumental magnitude 4.7 earthquake that truly shook the scientific community. Lasting over six hours, this unprecedented event allowed researchers to accurately infer the crust’s thickness throughout the entire planet.
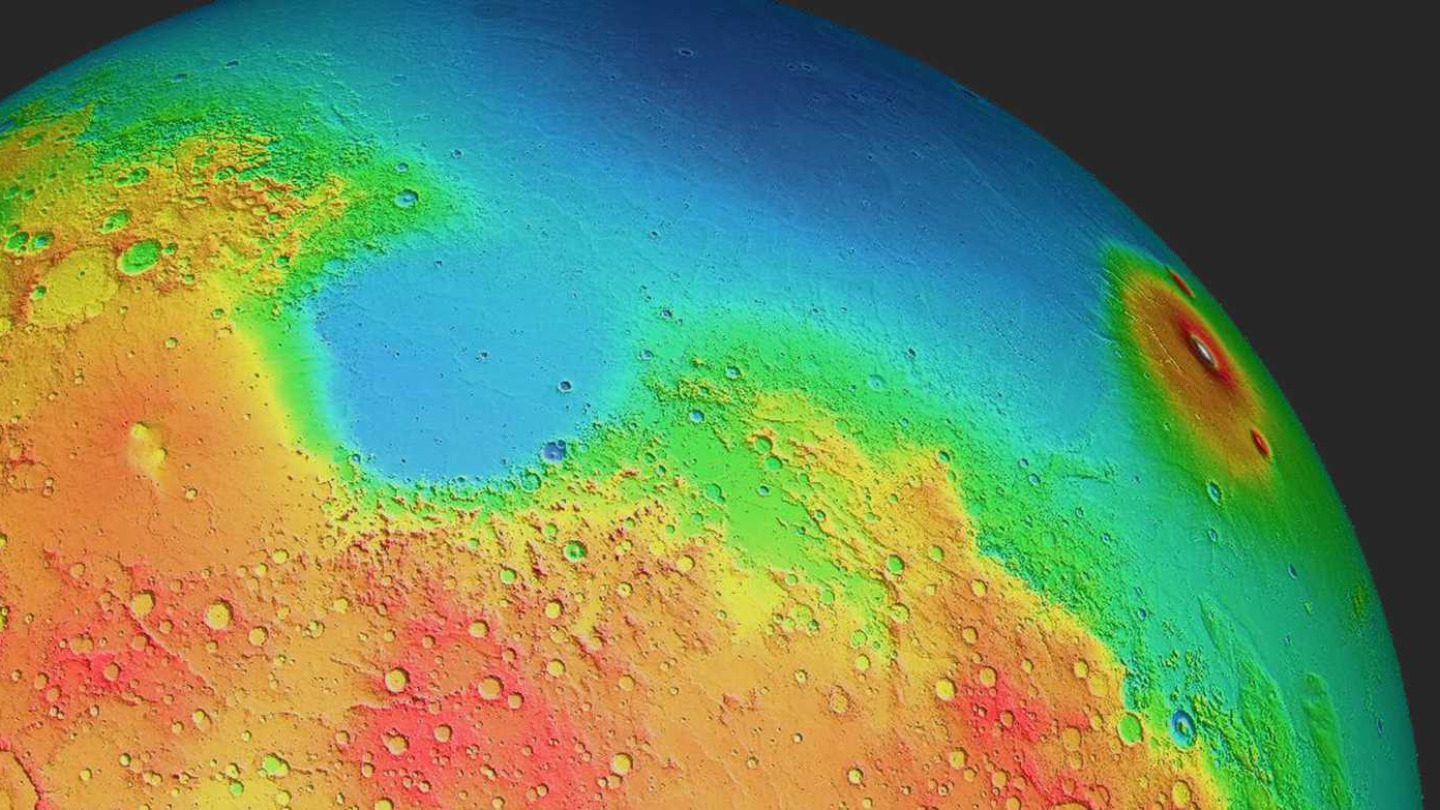
To the astonishment of the scientific community, the study revealed not only the unexpected thickness of the Martian crust but also its inconsistent nature across the Red Planet. These variations in crust thickness could potentially explain the known north-south elevation disparity observed on Mars. Data obtained from topological and gravity measurements by Mars orbiters have consistently shown that the planet’s northern hemisphere lies significantly lower than its southern counterpart. Density variations were initially considered a possible factor, with researchers speculating that rocks in the northern hemisphere may possess different densities than those in the southern hemisphere.
However, contrary to expectations, the study determined that the crust in the northern hemisphere is, in fact, thinner than in the southern hemisphere. This implies that the average densities of rocks in both hemispheres are likely similar. This groundbreaking revelation offers scientists a vital clue in unraveling the underlying causes of the pronounced elevation difference between Mars’ hemispheres.
New Study Finds Marsquake Data Unveils Martian Crust Thickness and Potential Volcanic Activity

The newfound knowledge of the crust’s depth has also enabled the research team to make another intriguing discovery. Through advanced calculations, they have determined that a significant portion of Mars‘ internal heat is likely generated within the crust itself. This internal heat is primarily attributed to the presence of radioactive elements such as potassium, uranium, and thorium. Remarkably, computer simulations indicate that an estimated 50 to 70 percent of these heat-producing elements reside within the crust rather than the underlying mantle. This finding lends strong support to the notion that certain regions of Mars may still harbor volcanic activity, debunking the long-held belief that the Red Planet is devoid of such geological processes.
The implications of these findings are profound, as they offer a fresh perspective on our understanding of Mars‘ geological evolution and potential habitability. By deciphering the mysteries concealed beneath the Martian surface, scientists are taking significant strides toward comprehending the planet’s complex history and uncovering its potential to sustain life.
As further investigations continue, the Martian crust will remain an object of intense study for planetary scientists worldwide. The groundbreaking research conducted by the InSight mission has not only deepened our knowledge of Mars but has also ignited a sense of wonder and excitement about the untold secrets that lie within our neighboring planet. With each discovery, the dream of unlocking the mysteries of Mars draws closer to becoming a reality.
Next Post: Deep-Sea Secrets Unveiled



